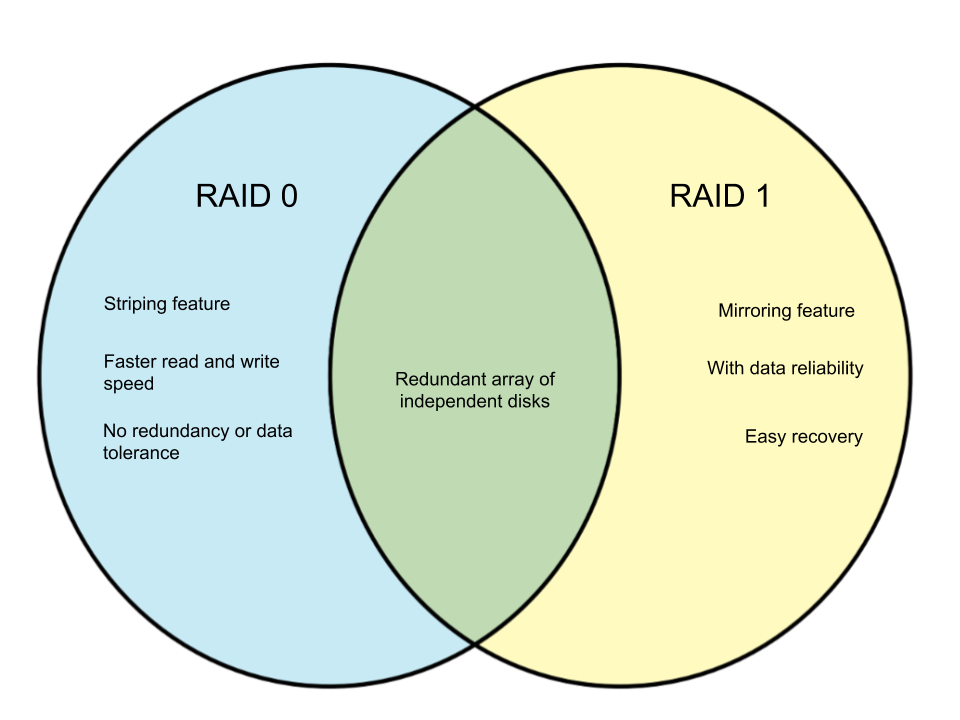
RAID stands for “redundant array of independent disks” and is a data storage technology that puts together multiple disk drive components into logical units. This is done for the purpose of improving performance or for data redundancy. There are different types to choose from like the RAID 0 and RAID 1. In this article, we will differentiate the RAID 0 and RAID 1.
RAID 0
One of the main differences between RAID 0 and RAID 1 is how they offer data redundancy. RAID 0 does not offer this but rather makes use of striping, or the splitting of data across all the drives. RAID 0 does not have mirroring or fault tolerance. In theory, it possesses faster read and write speeds and is applied when speed is the priority. RAID 0’s total storage is the same value as sum of all the individual hard drives’ storage capacity.
RAID 1
RAID 1 offers data redundancy with the use of mirroring. Albeit slower than RAID 0 in read and write speed, multiplexing can help mitigate this problem or result in the same performance as RAID 0. RAID 1 offers more data reliability and is used when data loss is absolutely unacceptable.
RAID 0 |
RAID 1 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Key feature | Striping | Mirroring |
| Data reliability | No guarantee | Better reliability |
| Read | Faster reading speed | Data reliability limits speed |
| Write | Faster writing speed | Data reliability limits speed |
| Storage | Equal to the total of the individual hard drives’ storage capability | Equal to the storage of any hard drive |
| Preferred when | Speed is prioritized | Data loss is unacceptable |
| Advantages | Full disk utilization, higher speed | Great performance with easy recovery |
| Disadvantages | Zero redundancy or data tolerance; risk of data loss | Limited storage capacity, reduced speed |
Venn Diagram