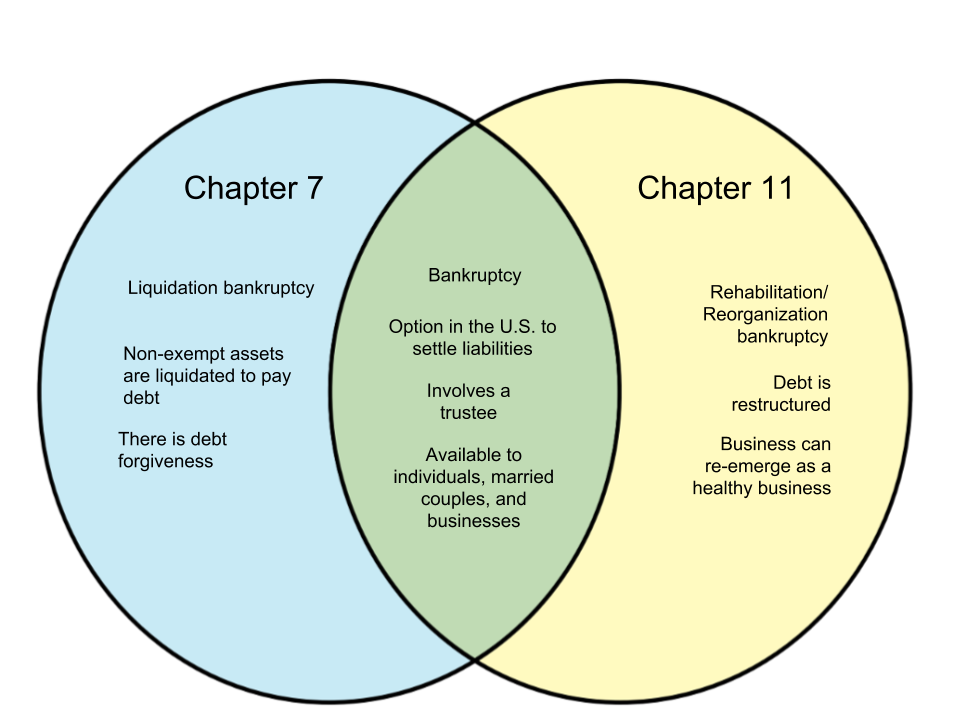
In the United States, there are different options when it comes to settling liabilities. In the instance that an entity is unable to pay for their debts using their present cash, they have the option of filing for bankruptcy. Chapter 7 and 11 bankruptcy are only two of the alternatives an entity may have. We will discuss their differences in this article.
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common form of bankruptcy. It is also known as liquidation bankruptcy. In this scenario, firms or entities are past the reorganization stage and are obliged to sell non-exempt assets to pay off their liabilities. Many liabilities are forgiven and personal assets are liquidated (sold) to repay whatever remaining debts they can pay off.
On the other hand, Chapter 11 organization is also known as reorganization or rehabilitation bankruptcy. This type of bankruptcy is more involved, allowing the entity to reorganize their debts and negotiate with creditors. This option allows them the possibility of re-emerging as a healthy, functioning firm or organization.
Chapter 7 |
Chapter 11 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A form of bankruptcy where the debtor liquidates their non-exempt/personal assets to pay for their liabilities | A form of bankruptcy where the debtor negotiates with creditors and reorganizes debt to settle liabilities |
| Also known as | Liquidation bankruptcy | Reorganization/rehabilitation bankruptcy |
| What happens here? | Personal/non-exempt assets are liquidated (sold) and the proceeds are used to pay creditors | The entity reorganizes/restructures their debt and contacts creditors to figure out an optimal way to settle liabilities |
| Does it involve a trustee? | Yes | Yes |
| What is the role of the trustee? | The trustee makes sure that the assets are secured and liquidated and that the proceeds are paid properly to the creditors | The trustee supervises the debtor’s assets to ensure the effective operation of the business |
| Does it involve liquidation of assets? | Yes, to the extent of non-exempt assets | No |
| Is there debt forgiveness? | Yes; this may occur when the proceeds from liquidation cannot cover all loans | No; Rather than forgiveness, the terms of the liabilities are changed to make payment more probable |
| Who can file for this? | Individuals, married couples, business organizations | Individuals, married couples, business organizations |
Venn Diagram