Cat5E and Cat6 are both twisted pair cables used for computers, servers, and the like. They are both made from copper wires and are used for similar purposes. In this article, we will distinguish how Cat5E and Cat6 cables differ from each other.
Cat5E
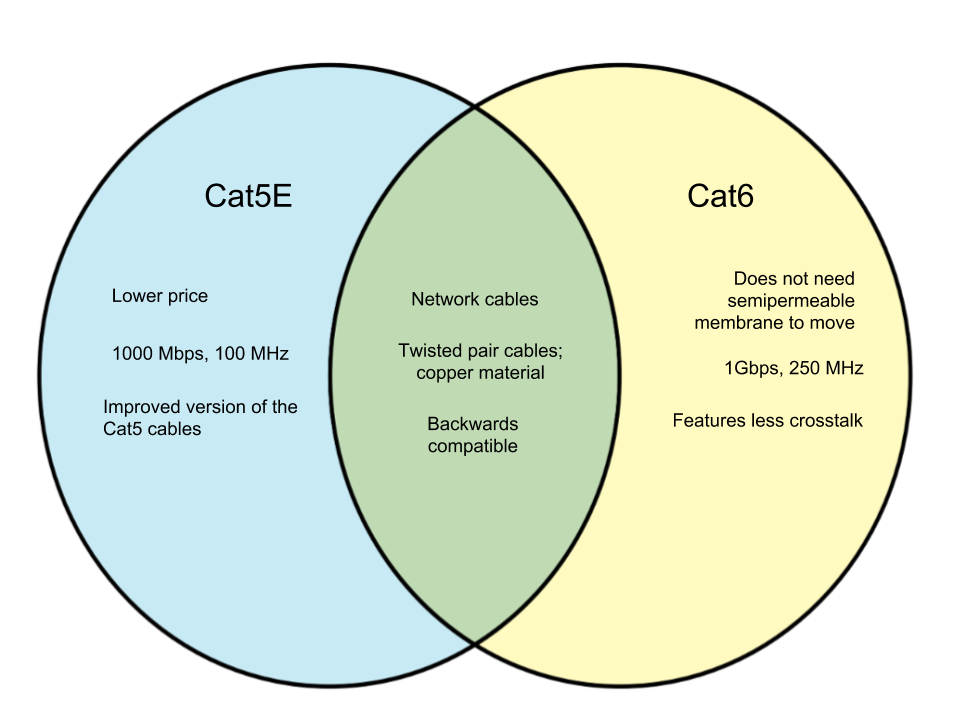
Cat5E stands for “Cat5 Enhanced” and is the improved version of the now obsolete Cat5 cable. A Cat5E cable can only support up to 1000BASE-T and can provide speeds to about 100 MHz. Just like Cat6, Cat5E is backwards compatible. It is generally more affordable than the Cat6 cable but also runs at lower frequencies. While many attest that Cat6 is always the better choice for network cables, Cat5E works just as well especially when it is simply for residential use. It is superior to its predecessor Cat5, is relatively affordable than Cat6, and is compatible with devices that may not be prepared for Cat6 just yet.
Cat6
Cat 6 stands for “Category 6” cables and boasts faster connection speeds, higher frequencies, and lower crosstalk that the Cat5E. The cables typically cost more than Cat5E, but CAT6 cables also have the same maximum length as the former – 100 meters. Cat6 cables are stronger and more rigid and thus often look thicker than Cat5E ones. They can handle up to 10 Gigabits of data but the bandwidth still tends to be limited to 164 feet. Regardless, many opt to invest in the Cat6 cables because Cat5Es also experience the same issue. People also want to “future-proof” their devices for residential or commercial purposes.
Cat5E |
Cat6 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Cat5 Enhanced | Category 6 |
| Brief overview | A network cable that is the improved version of the obsolete Cat5 cable | A network capable with less crosstalk and faster speeds; preferred by users who like to “future-proof” |
| Cost | About 20 to 30 cents per foot | About 20-30% more expensive than Cat5E |
| Maximum length | 100 meters | 100 meters |
| Bandwidth | 1000 Mbps | 1Gbps |
| Frequency | Up to 100 MHz | Up to 250 MHz |
| Performance/quality | Reduced crosstalk compared to Cat5 | Reduced crosstalk compared to Cat5E; higher SNR |
Venn Diagram