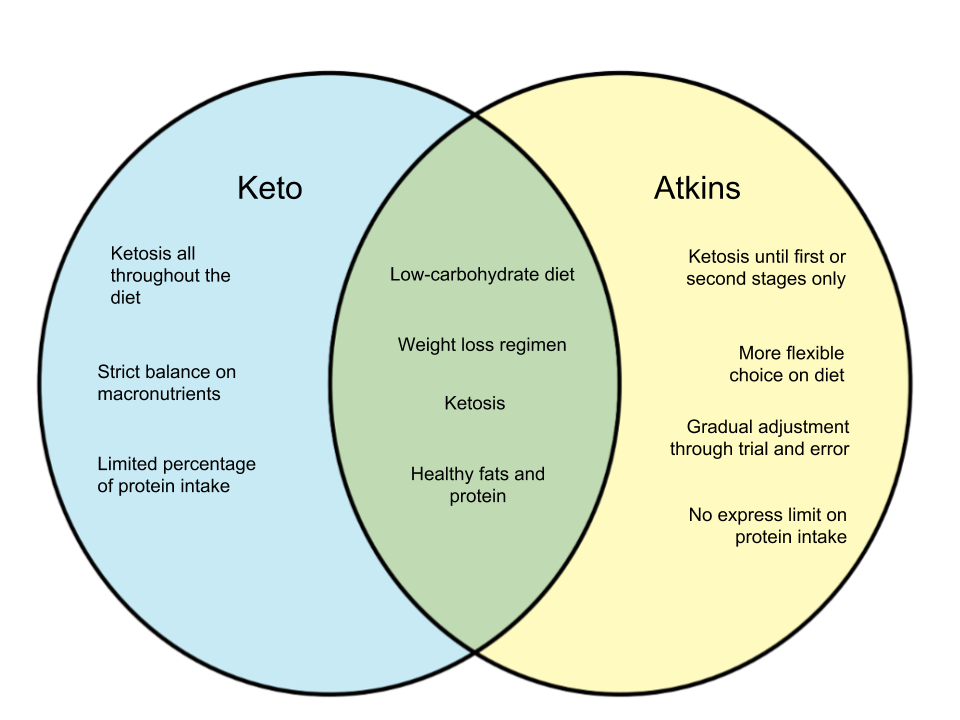
Among the carbohydrate intake reduction diets that are trending right now, it is perhaps the keto and atkins diets that are on the top of the pack. The two diet regimens also feature very similar qualities, but there are several distinctions between the two.
The keto or ketogenic diet has been present since the 1920s and started as a diet regimen for patients who suffer epilepsy. It has however, evolved into the diet that it is now. Keto diet focuses on the principle of ketosis, or the body’s natural process of burning fat rather than carbohydrates for fuel. The diet consists of reducing carbohydrate intake and consuming a variety of food types including healthy fats.
A strict balance is required in keto diets – balancing micronutrients in order to get the full benefits and avoiding side-effects is necessary. There are different types of keto diets, each type having a different proportion of carbs, protein, and carbohydrate intake.
The atkins diet was introduced by Dr. Robert Atkins who believed that obesity and excessive weight is attributed to consumption of processed carbohydrates like sugar and flour. Like the keto diet, its focus is reducing carbohydrate intake by consuming protein and healthy fats. The atkins diet began with the belief that consuming indulgent foods like bacon wouldn’t affect your weight as long as there were no carbohydrates present.
The atkins diet as evolved, but retains the principle that carbohydrates create spikes in blood sugar levels and encourage weight gain. It consists of four stages, with the induction stage limiting carb intake to 20-30 grams. Over the stages, the limit is gradually increased by trial and error, combining nutrition-rich carb food with protein and fat. Upon reaching the final stage, one would only need to maintain the diet regimen optimal to them.
Perhaps the most apparent difference between keto and atkins diets is the protein consumption. An atkins diet has no stated limit on the amount of protein intake, but keto diets typically limit the percentage of protein to 20 percent of one’s daily calories. The principle of ketosis, which also occurs in some parts of the atkins diet, only takes place in the first and second stages as well, while keto diets maintain that principle all throughout.
Keto |
Atkins |
|
|---|---|---|
| Full name | Ketogenic diet | Atkins diet or Atkins nutritional approach |
| Focus | Low-carbohydrates, energy from fats | Low-carbohydrates, energy from fats |
| Model | Principle of ketosis or burning stored fat in the body; burning fat for fuel rather than carbohydrates | Initial limit of 20-30 grams of carbohydrate intake among protein and healthy fat foods, gradual increase based on trial and error, maintenance of established eating routine |
| Benefits | Helps improve conditions and disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes, helps prevent and treat seizures, assists in rapid weight loss | Reduced hunger pangs, more flexible than keto, can improve cholesterol and lipid levels |
| Foods within the diet | Meat, plant-based meat, poultry, eggs, fish, dairy, healthy fats, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, berries | Meat, fatty fish and seafood, low-carb veggies, full-fat dairy products, eggs, avocados, nuts,seeds, healthy fats |
| Foods avoided | Whole grains, refined grains, refined sugars, candy, baked goods, sugary drinks, fruit juices, grains, low-fat dietary goods, fruits aside from a small amount of berries, beans, legumes, starchy vegetables | Sugar, grains, diet or low-fat foods, legumes, high-carb fruits like bananas and grapes during the first stage |
Venn Diagram